Discover the Future of Filmmaking: What’s Next for Cinema
The world of filmmaking is on the cusp of a profound transformation, driven by an accelerating pace of technological innovation and evolving audience expectations. What once seemed like science fiction — creating entire worlds digitally, interacting with narratives, or having AI assist in creative processes — is rapidly becoming reality. The future of cinema is not merely about bigger screens or louder sound systems; it is about fundamentally redefining how stories are conceived, produced, distributed, and ultimately experienced. This revolution promises to democratize creation, enhance immersion, and challenge traditional models of viewership, pushing the boundaries of what a “movie” can be.
Read Also: Antonio Chavez Trejo: Filmmaking and Resilience in Hollywood
From the earliest silent films to the advent of sound, color, and digital effects, filmmaking has always adapted to new technologies. However, the current wave of innovation, encompassing virtual production, artificial intelligence, and immersive realities, represents a paradigm shift. These advancements are not just incremental improvements; they are foundational changes that enable filmmakers to achieve previously impossible visions, streamline complex workflows, and engage audiences in entirely new ways. The journey into the future of filmmaking promises a landscape of unprecedented creative freedom and a more dynamic relationship between creators and viewers, reshaping the very essence of cinematic storytelling.
How Is Virtual Production Reshaping Film Sets?
Virtual production (VP) stands as one of the most significant advancements revolutionizing how films are made, fundamentally altering the traditional on-set experience. Unlike conventional green screen setups where visual effects are added entirely in post-production, VP uses large LED volumes (or walls) that display real-time rendered digital environments behind actors. Directors, cinematographers, and actors can see the virtual world live on set, allowing for immediate feedback on lighting, camera angles, and performances. This immediate visualization dramatically enhances the creative process, making it more intuitive and collaborative, and blurring the lines between physical and digital sets.
Key components of virtual production include high-resolution LED screens, powerful game engines (like Unreal Engine) that render the digital environments in real time, and sophisticated camera tracking systems. As the physical camera moves, the virtual background adjusts dynamically, creating perfect perspective and parallax, convincing the eye that the actors are truly within the digital world. This real-time integration means that many visual effects are “baked in” during production, significantly reducing the amount of complex and time-consuming work traditionally done in post-production, such as rotoscoping and compositing.

Photo Credit: Unsplash.com
The benefits of virtual production extend beyond just visual effects. It offers filmmakers unprecedented creative control and flexibility. Directors can change settings, time of day, or lighting conditions with a few clicks, without the need for expensive and time-consuming location shoots or set builds. Actors perform within believable environments, leading to more natural and consistent eye-lines and performances. While initial setup costs can be substantial, VP often proves more cost-effective for complex productions in the long run by saving on travel, traditional set construction, and extensive post-production, truly redefining the physical and digital boundaries of a film set.
What Role Will Artificial Intelligence Play in Filmmaking?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force across all stages of filmmaking, from pre-production to distribution. In the early stages, AI-powered tools can analyze scripts to identify plot holes, character inconsistencies, and even predict potential box office performance. Generative AI models can assist with storyboarding, concept art generation, and mood board creation, allowing filmmakers to visualize their ideas much faster and more affordably. This capability empowers creative teams to iterate on visual concepts with unprecedented speed, transforming weeks of manual effort into hours.
During production and post-production, AI’s influence becomes even more pronounced. AI can assist with tasks like automated video editing, suggesting cuts, optimizing shot sequences, and even creating rough edits. In visual effects, AI is revolutionizing the creation of realistic CGI characters and environments, automating processes like rotoscoping, motion tracking, and even generating synthetic footage that is increasingly indistinguishable from real-world captures. AI-powered color grading tools can help achieve a consistent look and feel across an entire film, streamlining a traditionally meticulous process and allowing filmmakers to focus more on creative nuances rather than technical adjustments.
However, the integration of AI also raises important questions about the future of human labor and creativity in the film industry, as highlighted by recent industry strikes. While AI can automate repetitive or technical tasks, the human element of storytelling, emotional depth, and unique artistic vision remains irreplaceable. The future likely lies in a collaborative model, where AI serves as a powerful tool that augments human creativity, accelerating workflows and enabling filmmakers to realize more ambitious visions, rather than entirely replacing human roles. AI’s true potential lies in empowering creators, making filmmaking more efficient, and potentially democratizing high-quality content creation for independent filmmakers.
How Will Immersive and Interactive Experiences Change Viewing?
The future of cinema is increasingly moving beyond the traditional flat screen, embracing immersive and interactive experiences that redefine how audiences engage with stories. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are at the forefront of this shift, offering pathways for viewers to step into narratives rather than merely observing them. VR cinema, with its 360-degree environments and headset-driven immersion, can place audiences directly at the center of the action, allowing them to look around and explore a scene as if they were physically present, leading to a profound sense of presence and empathy.
Interactive storytelling is another significant trend, giving audiences agency within the narrative. This ranges from “choose-your-own-adventure” style films where viewer decisions impact the plot, to more subtle forms of interaction where a viewer’s gaze or movement might influence subtle elements of the story or environment. This shift from passive consumption to active participation promises a highly personalized and engaging viewing experience, making each viewing potentially unique. While still in nascent stages for mainstream cinema, platforms are experimenting with branching narratives and adaptive content that responds to viewer input, blurring the lines between film and gaming.
Beyond individual headsets, immersive audio technologies like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X are creating multi-dimensional soundscapes that envelop the audience, making sounds appear to come from specific points in a 3D space. Coupled with haptic feedback systems, specialized seating, and even environmental effects (like wind or scent), these technologies transform the movie theater into a multi-sensory environment. The goal is to create a complete sensory immersion that deepens the emotional connection to the story, turning a cinema visit into a truly memorable event that traditional home viewing cannot replicate, thus ensuring the continued relevance of the theatrical experience.
What Are the New Frontiers in Film Distribution?
The landscape of film distribution is undergoing a profound shift, moving away from traditional theatrical exclusivity towards a more diverse and fragmented ecosystem. The rise of streaming platforms (OTT – Over The Top services) has fundamentally altered consumer viewing habits, giving audiences unprecedented access to vast libraries of content on demand. Direct-to-streaming releases, once considered a last resort, have become a viable and often preferred strategy for many films, especially after recent global events accelerated this trend. This shift challenges the long-standing “theatrical window” and forces studios and exhibitors to re-evaluate their release strategies.
Hybrid release models, where films premiere simultaneously in theaters and on streaming platforms, or with significantly shortened theatrical windows, are becoming increasingly common. This allows studios to maximize revenue by catering to different audience preferences: those who prefer the communal big-screen experience and those who opt for home convenience. For independent filmmakers, digital distribution platforms and blockchain technologies offer new avenues for reaching global audiences directly, bypassing traditional gatekeepers and potentially enabling more democratic revenue-sharing models. This empowerment of indie creators is a significant step towards a more diverse cinematic landscape.
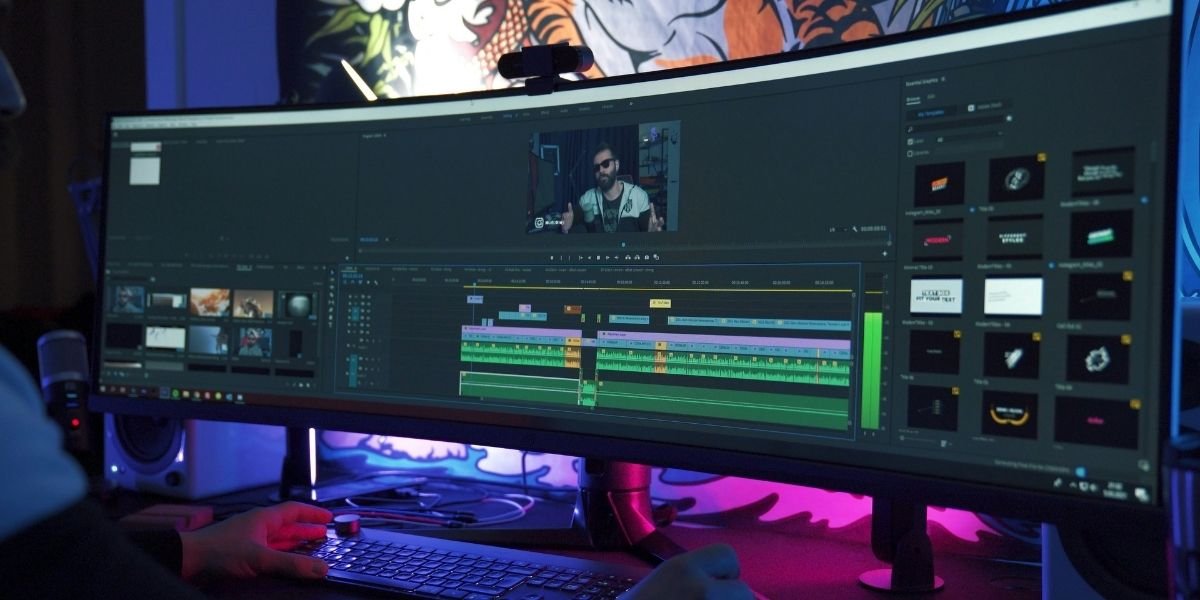
Photo Credit: Unsplash.com
The future of film distribution will likely involve continued experimentation with windowing strategies, personalized content delivery, and new monetization models, including advertising-supported video on demand (AVOD) and innovative subscription tiers. Cinemas, to remain competitive, are investing in premium formats (IMAX, Dolby Cinema), enhanced seating, and unique immersive experiences that differentiate them from home viewing. The competition for audience attention is fiercer than ever, driving innovation not just in how films are made, but in how they are delivered to viewers worldwide, emphasizing convenience, choice, and immersive quality.
How is Filmmaking Becoming More Sustainable?
As the global entertainment industry becomes more aware of its environmental footprint, sustainable filmmaking is emerging as a critical trend, shaping future production practices. Traditional film production can be resource-intensive, involving significant energy consumption, material waste from sets and props, extensive travel, and substantial carbon emissions. The future of filmmaking is increasingly green, with a growing commitment to reducing this environmental impact across all stages of production. This involves a conscious effort to adopt eco-friendly practices, from pre-production planning to post-release distribution.
On sets, sustainable practices include the widespread adoption of energy-efficient LED lighting, which consumes significantly less power than traditional lights, and the use of renewable energy sources like solar generators. Waste reduction programs focus on minimizing single-use plastics, implementing comprehensive recycling, and repurposing or donating set materials, costumes, and props after production. Transportation is another key area, with efforts to reduce flights, encourage carpooling, and utilize electric or hybrid vehicles for crew movements. Even catering is becoming more sustainable, with an emphasis on locally sourced, plant-based meals and reduced food waste.
Read Also: How Post-Production Technology Is Transforming Filmmaking
Beyond the physical production, the digital realm also plays a role in sustainability. Digital distribution methods significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing and transporting physical media like DVDs and Blu-rays. Furthermore, the rising awareness of climate change is influencing narrative choices, with more filmmakers weaving environmental themes into their stories, inspiring audiences to consider their own impact. Organizations and initiatives like Green Production Guide and Albert are providing tools, certifications, and resources to help productions track and lower their carbon footprint, fostering a collective movement towards a more environmentally responsible and sustainable future for the entire filmmaking industry.















